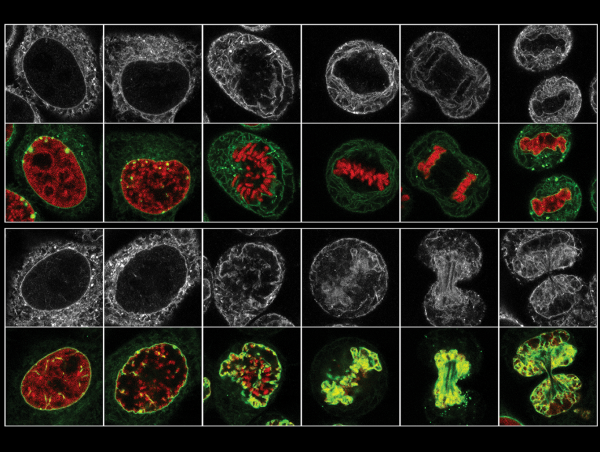
Figure 2 from The nuclear envelope and the architecture of the nuclear Biology Diagrams During telophase, the nuclear envelope (NE) reforms around daughter nuclei to ensure proper segregation of nuclear and cytoplasmic contents[-] . NE reformation requires the coating of chromatin by membrane derived from the Endoplasmic Reticulum and a

The nuclear envelope is a dynamic structure that is disassembled and reassembled during 'open' mitosis in higher eukaryotes. These mitotic changes are subject to both spatial and temporal control
The nuclear envelope: form and reformation Biology Diagrams
The ESCRT-III complex is implicated in the reformation of the nuclear envelope; the CHMP2A component of ESCRT-III is directed to the forming nuclear envelope through classical ESCRT-assembly

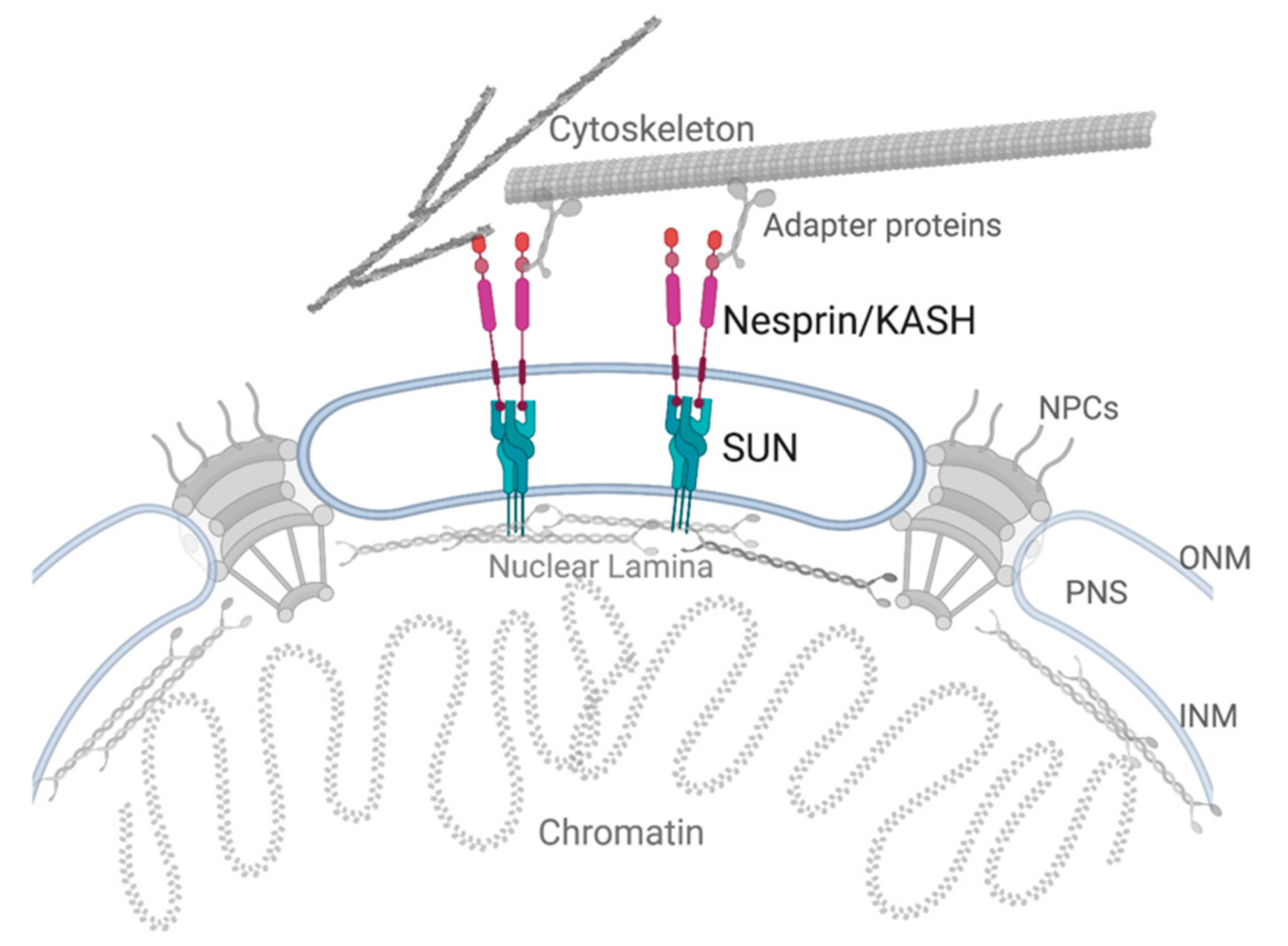
The nuclear envelope: form and function The INM, ONM and pore membrane are each intimately associated with distinct proteinaceous structures; these connections ensure the integrity of the nuclear environment and aid in coordinating cellular events.

III controls nuclear envelope reformation Biology Diagrams
This review aims at assessing the current understanding of how phosphatases contribute to the remodelling of the nuclear envelope during its disassembling and reformation after cell division and how errors in this process may lead to the development of diseases. The membrane system that encloses genomic DNA is referred to as the nuclear envelope. However, with emerging roles in signaling and gene expression, these membranes clearly serve as more than just a physical barrier separating the nucleus and cytoplasm. Recent progress in our understanding of nuclear envelope architecture and composition has also revealed an intriguing connection between During cell division, remodeling of the nuclear envelope (NE) enables chromosome segregation by the mitotic spindle[] . The reformation of sealed nuclei requires Endosomal Sorting Complexes Required for Transport (ESCRTs) and LEM2, a transmembrane ESCRT